Table of Contents
关于
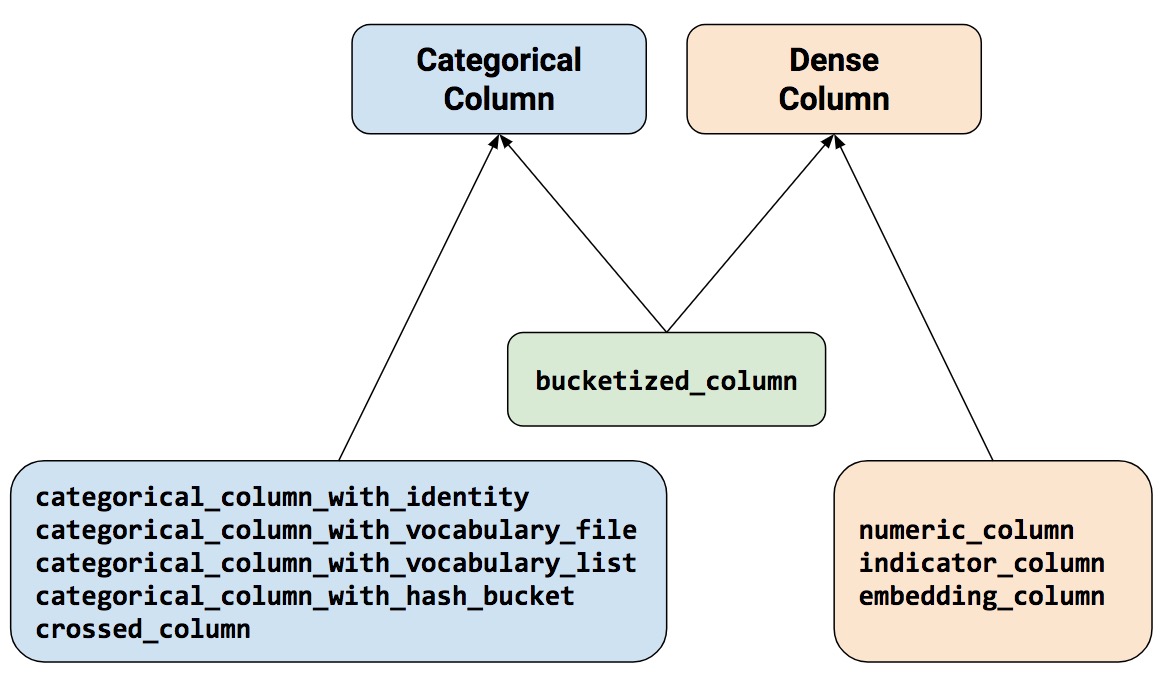
Numeric column
创建单个标量特征列
# Defaults to a tf.float32 scalar. numeric_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key="SepalLength", dtype=tf.float64)
创建向量特征列
# Represent a 10-element vector in which each cell contains a tf.float32. vector_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key="Bowling", shape=10)
Bucketized column
分桶的列,将数值按照桶划分成多个类别特征
# First, convert the raw input to a numeric column. numeric_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column("Year") # Then, bucketize the numeric column on the years 1960, 1980, and 2000. bucketized_feature_column = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column( source_column = numeric_feature_column, boundaries = [1960, 1980, 2000])
Categorical identity column
相当于对整数做 onehot
# Create categorical output for an integer feature named "my_feature_b", # The values of my_feature_b must be >= 0 and < num_buckets identity_feature_column = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity( key='my_feature_b', num_buckets=4) # Values [0, 4) # In order for the preceding call to work, the input_fn() must return # a dictionary containing 'my_feature_b' as a key. Furthermore, the values # assigned to 'my_feature_b' must belong to the set [0, 4). def input_fn(): ... return ({ 'my_feature_a':[7, 9, 5, 2], 'my_feature_b':[3, 1, 2, 2] }, [Label_values])
Categorical vocabulary column
对字符串做字典映射,然后 onehot, 可以指定列表,或者文件
# Given input "feature_name_from_input_fn" which is a string, # create a categorical feature by mapping the input to one of # the elements in the vocabulary list. vocabulary_feature_column = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list( key=feature_name_from_input_fn, vocabulary_list=["kitchenware", "electronics", "sports"]) # Given input "feature_name_from_input_fn" which is a string, # create a categorical feature to our model by mapping the input to one of # the elements in the vocabulary file vocabulary_feature_column = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file( key=feature_name_from_input_fn, vocabulary_file="product_class.txt", vocabulary_size=3)
Hashed Column
Hash取模, 返回 category column
# pseudocode feature_id = hash(raw_feature) % hash_bucket_size
hashed_feature_column = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_hash_bucket( key = "some_feature", hash_bucket_size = 100) # The number of categories
Crossed column
特征交叉
def make_dataset(latitude, longitude, labels): assert latitude.shape == longitude.shape == labels.shape features = {'latitude': latitude.flatten(), 'longitude': longitude.flatten()} labels=labels.flatten() return tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((features, labels)) # Bucketize the latitude and longitude using the `edges` latitude_bucket_fc = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column( tf.feature_column.numeric_column('latitude'), list(atlanta.latitude.edges)) longitude_bucket_fc = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column( tf.feature_column.numeric_column('longitude'), list(atlanta.longitude.edges)) # Cross the bucketized columns, using 5000 hash bins. crossed_lat_lon_fc = tf.feature_column.crossed_column( [latitude_bucket_fc, longitude_bucket_fc], 5000) fc = [ latitude_bucket_fc, longitude_bucket_fc, crossed_lat_lon_fc] # Build and train the Estimator. est = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(fc, ...)
Indicator and embedding columns
onehot编码
tf.feature_column.indicator_column(categorical_column)
embedding列
tf.feature_column.embedding_column( categorical_column=categorical_column, dimension=embedding_dimensions)
Passing feature columns to Estimators
tf.estimator.LinearClassifier和tf.estimator.LinearRegressor: 所有的特征列.tf.estimator.DNNClassifier和tf.estimator.DNNRegressor: 只支持 dense 列. 其他特征列必须转成indicator_column或者embedding_column.tf.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedClassifier和tf.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedRegressor:- The linear_feature_columns argument accepts any feature column type.
- The dnn_feature_columns argument only accepts dense columns.