Table of Contents
简介
Spark Streaming 将流数据按照时间离散化,每单位时间一个batch!这是和其他流处理系统不同的地方。
好处是效率更高,缺点是牺牲了一定的实时性。
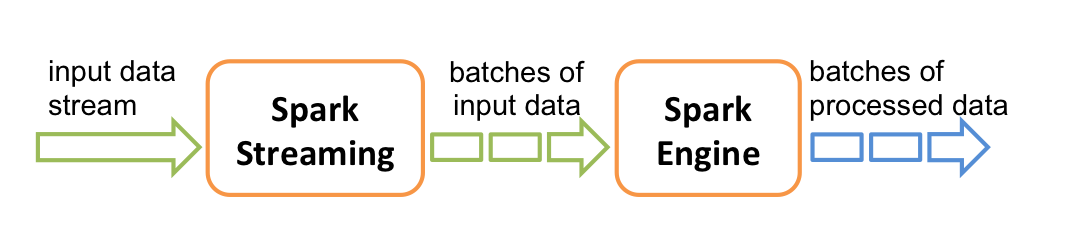
StreamingContext
import org.apache.spark._ import org.apache.spark.streaming._ val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName(appName).setMaster(master) val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
每一个 Batch 是一个DStream对象,一个 DStream 对象实际上是一些列的RDD。
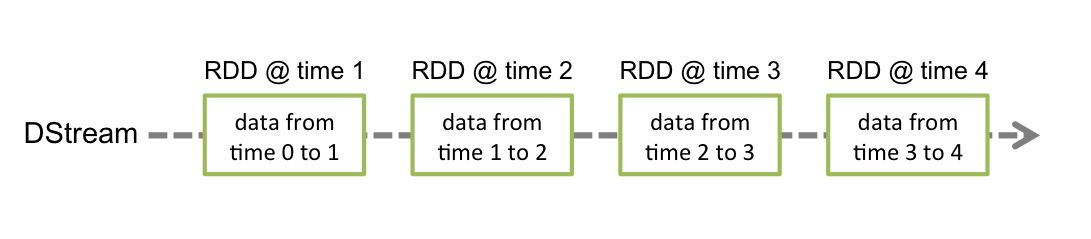
Input DStreams and Receivers
- 输入源:
- 基本数据源:文件系统和套接字连接
- 高级源:Kafka, Flume, Kinesis, etc
- 每一个 DStream 都有至少一个 Receiver,本地模式运行时,线程数目应该多余源的数目。
基本源
- 文件系统:
streamingContext.fileStream[KeyClass, ValueClass, InputFormatClass](dataDirectory) - RDD队列:
streamingContext.queueStream(queueOfRDDs) - Custom Receivers
DStreams 的变换操作
- 支持RDD上类似的变换操作。
UpdateStateByKey 操作
用于维护一个持续的状态,状态可以是任意数据类型。
def updateFunction(newValues: Seq[Int], runningCount: Option[Int]): Option[Int] = { val newCount = ... // add the new values with the previous running count to get the new count Some(newCount) } val runningCounts = pairs.updateStateByKey[Int](updateFunction _)
Transform 操作
直接对rdd进行操作
val spamInfoRDD = ssc.sparkContext.newAPIHadoopRDD(...) // RDD containing spam information val cleanedDStream = wordCounts.transform { rdd => rdd.join(spamInfoRDD).filter(...) // join data stream with spam information to do data cleaning ... }
Window 操作
- window 大小
- sliding 大小
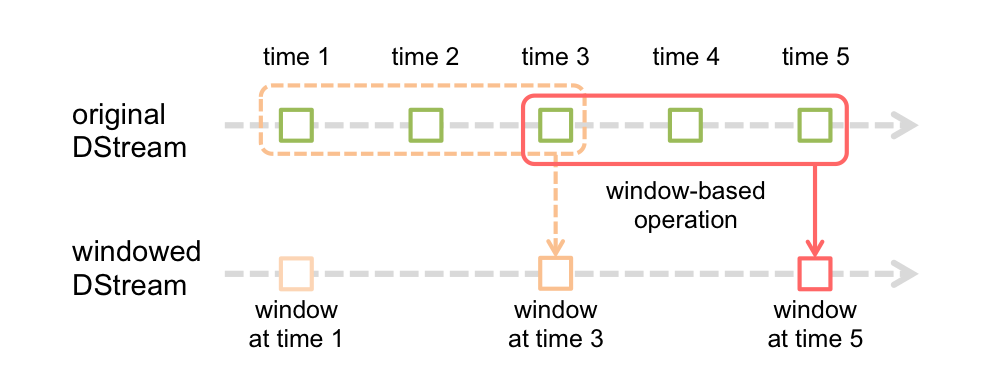
// Reduce last 30 seconds of data, every 10 seconds val windowedWordCounts = pairs.reduceByKeyAndWindow((a:Int,b:Int) => (a + b), Seconds(30), Seconds(10))
join 操作
- Stream-stream joins 将两个 DStream join到一起,实际上是在每个时间隙,将两个 DStream 的 RDD join到一起。