关于
见论文 http://cn.arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450
摘要
Batch Normalization 难以应用在RNN,因为是基于输入的batch进行归一化,
而RNN输入每次都只有一个!
导言
分布式神经网络:Jeffrey Dean, Greg Corrado, Rajat Monga, Kai Chen, Matthieu Devin, Mark Mao, Andrew Senior, Paul Tucker, Ke Yang, Quoc V Le, et al. Large scale distributed deep networks. In NIPS, 2012.
In addition to training time improvement, the stochasticity from the batch statistics serves as a regularizer during training.
实际上就是讲 BN 对batch的归一化变成了对神经网络某一层进行归一化。
- BN:一个batch使用相同的均值和方差,但是不同神经元不同!对batch大小有要求,不能太小!对于RNN,需要在每一个时隙单独保存均值和方差参数!
- LN:同一层神经元使用相同的均值和方差,但是不同样本不同!对batch大小没有要求,适用于RNN,不需要单独保存参数,隐层数目不能太小吧
$$
\mu^l = \frac{1}{H} \sum_{i=1}^H a_i^l \\
\sigma^l = \sqrt{\frac{1}{H} \sum_{i=1}^H (a_i^l-\mu^l)^2 }.
$$
H代表该层的神经元个数!
对于标准的RNN,$(a^t = W_{hh}h^{t-1} + W_{xh} x^t)$。
$$
h^t = f\left[\frac{g}{\sigma} \odot (a^t-\mu^t)+ b \right]
$$
$(b, g)$ 是两个参数,需要学习,和BN中类似。
不变性分析
BN,LN,WN(weight Normalization) 都可以用下述形式表示:
$$
h_i = f(\frac{g_i}{\sigma_i}(a_i-\mu_i) + b_i)
$$
对于WN,$(\mu=0, \sigma = || w||_2)$
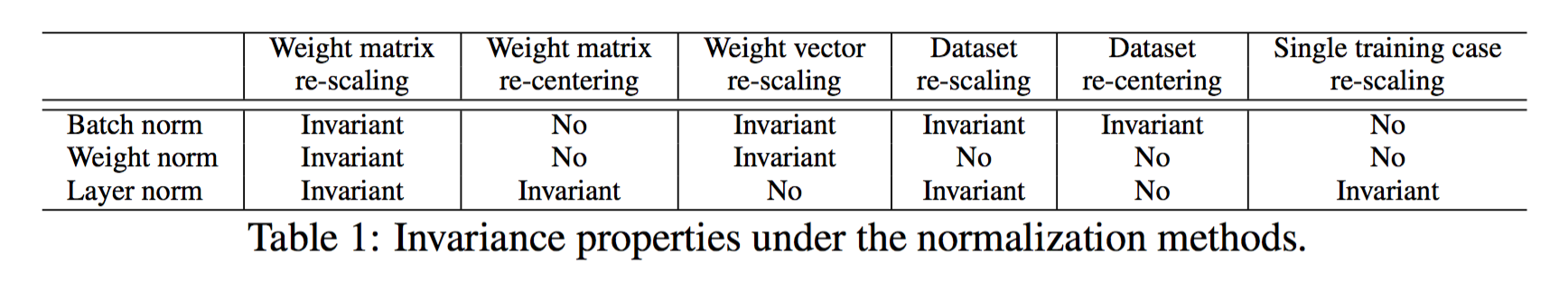
- Weight matrix re-scaling and re-centering: 对权值矩阵进行变换:$(W \rightarrow \delta W + \gamma)$
- Weight vector re-scaling and re-centering: 指对权值矩阵的某一个向量做上述仿射变换,BN和WN是不变得,因为他们每个神经元都有自己的归一化参数,而LN是变得,因为它所有神经元共用同一组规划参数。
- Data re-scaling and re-centering:指对数据集的归一化操作,LN对单个数据的rescaling也是不变的!(因为它归一化的时候仅考虑一个样本!)
Geometry of parameter space during learning
Under the KL divergence metric, the parameter space is a Riemannian manifold?!!
KL距离下的黎曼度规可以用Fisher信息矩阵的二阶近似
$$
ds^2 = D_{KL}(P(y|x;\theta) || P(y|x; \theta + \delta)) \approx \frac{1}{2}\delta^T F(\theta) \delta \\
F(\theta) = \mathbb{E}_{x\sim P(x), y\sim P(y|x)} \left[ \frac{\partial \log P(y|x;\theta)}{\partial \theta} \frac{\partial \log P(y|x;\theta)}{\partial \theta}^T \right]
$$
GLM 的几何分析
广义线性模型对数似然函数表示为LN的输入a的形式
$$
\log P(y|x;w,b) = \frac{(a+b) y - \eta(a + b)}{\phi} + c(y, \phi) \\
\mathbb{E}[y| x] = f(a+b) = f(w^T x + b), \\
Var[y| x] = \phi f'(a+b)
$$
这里 $(f)$ 是函数$(\eta')$,为GLM的均值函数。
假设有多个独立的response变量,$(y = [y_1, ..., y_H])$,对应多分模型参数$(\theta = [w_1^T, b_1, ..., w_H^t, b_H^T]^T)$,
将对数似然函数代入Fisher信息矩阵,并对$(y)$求期望,可得
$$
F(\theta) = \mathbb{E}_{x\sim P(x)} \left[ \frac{Cov[y|x]}{\phi^2} \otimes \left[ \begin{matrix}
xx^T & x \\
x^T & 1
\end{matrix} \right] \right]
$$
采用归一化方法后,将额外的参数g加到参数列表中,$(\theta = vec([W, \mathbf{b}, \mathbf{g}]^T))$
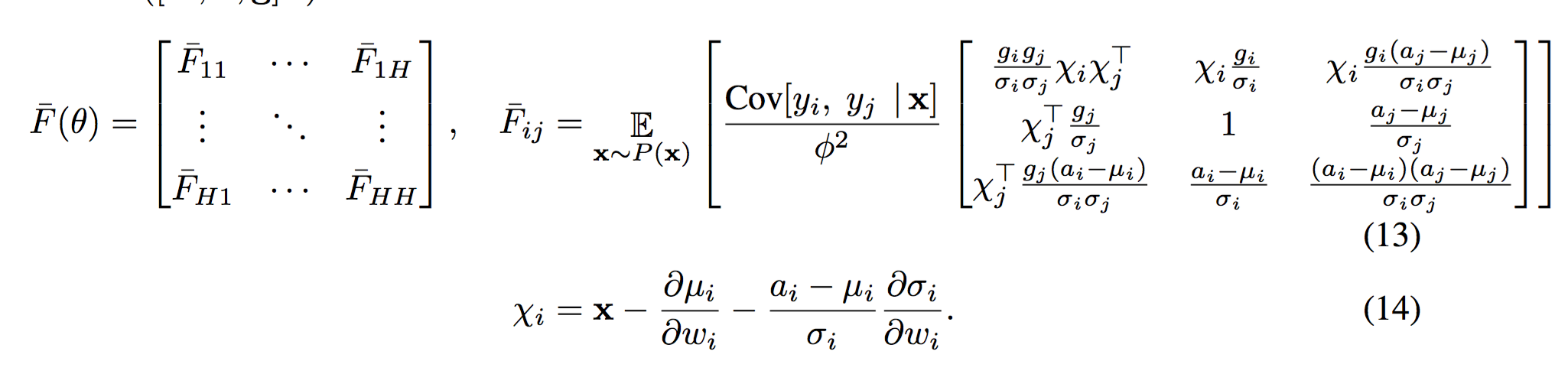
for the same parameter update in the normalized model, the norm of the weight vector effectively controls the learning rate for the weight vector.
have an implicit “early stopping” effect on the weight vectors and help to stabilize learning towards convergence.
Riemannian metric along the magnitude of the incoming weights for the standard GLM is scaled by the norm of its input, whereas learning the gain parameters for the batch normalized and layer normalized models depends only on the magnitude of the prediction error. Learning the magnitude of incoming weights in the normalized model is therefore, more robust to the scaling of the input and its parameters than in the standard model.
归一化改变曲率?还学习到了输入幅度?!
实验结果
在多个任务上进行试验:对RNN和全连接网络有效,可以加速收敛,但是CNN上的结果不如BN,作者认为CNN神经元之间的统计特性相差太大导致的,
因为每个神经元都只链接上一层一小块区域,从而导致同一层的神经元统计特性相差很大!但是作者没有报道具体结果,LN比BN差多少也不得而知。
- Order embeddings of images and language: Ivan Vendrov, Ryan Kiros, Sanja Fidler, and Raquel Urtasun. Order-embeddings of images and language.
ICLR, 2016. - Teaching machines to read and comprehend:Karl Moritz Hermann, Tomas Kocisky, Edward Grefenstette, Lasse Espeholt, Will Kay, Mustafa Suleyman,
and Phil Blunsom. Teaching machines to read and comprehend. In NIPS, 2015. - Skip-thought vectors:Ryan Kiros, Yukun Zhu, Ruslan R Salakhutdinov, Richard Zemel, Raquel Urtasun, Antonio Torralba, and Sanja
Fidler. Skip-thought vectors. In NIPS, 2015. - Modeling binarized MNIST using DRAW:K. Gregor, I. Danihelka, A. Graves, and D. Wierstra. DRAW: a recurrent neural network for image generation. arXiv:1502.04623, 2015.
- Handwriting sequence generation:Marcus Liwicki and Horst Bunke. Iam-ondb-an on-line english sentence database acquired from handwritten text on a whiteboard. In ICDAR, 2005.
- Permutation invariant MNIST