关于
长期以来,RNN、LSTM及其变种模型被应用到自然语言处理方面。
近年来,将CNN应用到自然处理方面也有一些工作。
字母级别的CNN
主要论文:Character-level Convolutional Networks for Text Classification, Xiang Zhang, Junbo Zhao, Yann LeCun, 2016
目前文本分类研究已从设计好的特征转为选择好的分类模型。
目前,所有的文本分类技术都是以词为基本单位的,简单统计词和词的n-gram就可以做到最好的效果。
T. Joachims. Text categorization with suport vector machines: Learning with many relevant features. In
Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Machine Learning, pages 137–142. Springer-Verlag,
1998.
卷积网络很适合从raw signals中提取有用的特征,已在机器视觉和语音识别等任务中得到应用。
而实际上,time-delay networks 早在深度学习出来以前就将卷积网络应用到序列数据之上。
- L. Bottou, F. Fogelman Soulie, P. Blanchet, and J. Lienard. Experiments with time delay networks and ´
dynamic time warping for speaker independent isolated digit recognition. In Proceedings of EuroSpeech
89, volume 2, pages 537–540, Paris, France, 1989. - R. Johnson and T. Zhang. Effective use of word order for text categorization with convolutional neural
networks. CoRR, abs/1412.1058, 2014.
在这篇文章中,将文本当做字符为单位的序列数据,然后应用时间卷积网络(temporal (one-dimensional) ConvNets)。
卷积网络应用到文本和自然语言处理已有一些研究了,它既可以应用到连续值的embedding数据,也可以应用到离散值的embedding数据,
并不需要任何语法和语义信息!其结果也和经典的方法具有可比性!
- C. dos Santos and M. Gatti. Deep convolutional neural networks for sentiment analysis of short texts. In
Proceedings of COLING 2014, the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical
Papers, pages 69–78, Dublin, Ireland, August 2014. Dublin City University and Association for
Computational Linguistics. - Y. Kim. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference
on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 1746–1751, Doha, Qatar,
October 2014. Association for Computational Linguistics. - R. Johnson and T. Zhang. Effective use of word order for text categorization with convolutional neural
networks. CoRR, abs/1412.1058, 2014
使用字母级别特征来做NLP也有一些早起工作,能够在POS tagging和IR方面的提升。This article is the first to apply ConvNets only on characters.
可以简化特征工程,能够学到拼写错误和emoji符号。
- character-level n-grams with linear classifiers: I. Kanaris, K. Kanaris, I. Houvardas, and E. Stamatatos. Words versus character n-grams for anti-spam filtering. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools, 16(06):1047–1067, 2007
- incorporating character-level features to ConvNets: C. D. Santos and B. Zadrozny. Learning character-level representations for part-of-speech tagging. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-14), pages 1818–1826, 2014
- Y. Shen, X. He, J. Gao, L. Deng, and G. Mesnil. A latent semantic model with convolutional-pooling structure for information retrieval. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pages 101–110. ACM, 2014.
模型
采用一位的卷积和max-pooling!
- 对 Pooling 的分析文章:Y.-L. Boureau, J. Ponce, and Y. LeCun. A theoretical analysis of feature pooling in visual recognition.
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), pages 111–118, 2010 - ReLU 最早文章:V. Nair and G. E. Hinton. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings
of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), pages 807–814, 2010
数据
字母通过one-hot编码为70维向量,包括26个字母,10个数字,33个其他字符和换行符。字符包括:
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789
-,;.!?:’’’/\|_@#$%ˆ&*˜‘+-=<>()[]{}
对中文的处理,将中文转换为拼音 pypingyin。
设计细节
模型设计
6层卷积层+3层全连接层,kernel维度为7和3,pool维度为3。
数据增强
用近义词进行替换,增加样本!平移不适应于这里!
和传统方法比较:
- Bag of word with TFIDF
- Bag of n-gram with TFIDF
- Bag of means with word embedding
深度学习方法比较:
- word-based CNN:
- LSTM:
结论
数据集达到百万量级才能观察到这种方法的优势,数据集小的时候还是 n-gram with TFIDF 好
There is no free lunch. Our experiments once again verifies that there is not a single machine
learning model that can work for all kinds of datasets. The factors discussed in this section could all
play a role in deciding which method is the best for some specific application.
Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Natural Language Processing
论文: Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Natural Language Processing, Le Cun, 2016
目前RNN,LSTM,CNN应用到NLP中的深度和在CV中相比,还比较浅,这篇文章提出一种方案可以从字母级别开始学习,模型深度达到29层!
CNN:将特征提取和分类进行联合训练!除了自动特征提取之外,还可以根据具体任务调整特征!
目前主流的方法,是利用 word embedding + RNN(LSTM)。
- Martin Sundermeyer, Ralf Schlüter, and Hermann Ney. LSTM neural networks for language
modeling. In Interspeech, 2012. - Ilya Sutskever, Oriol Vinyals, and Quoc V. Le. Sequence to sequence learning with neural
networks. In NIPS, pages 3104–3112, 2014.
作者argue:
- 作者认为 LSTM 是一种一般的序列学习方法,缺乏领域特性 "lacking task specific structure"
- 单词按照顺序进入,第一个单词变换了很多次,而最后一个词只变换一次! => bidirectional LSTM
- 深度不够,超过4层就没啥提升了,尽管加入了 dropout 正则化!
观点:
We believe that the challenge in NLP is to develop deep architectures which are able to learn hierarchical
representations of whole sentences, jointly with the task.
recursive neural network : 在RNN上增加了序列融合的顺序结构(树结构),RNN可以看做一个特殊的 recursive NN.
- Richard Socher, Jeffrey Pennington, Eric H. Huang, Andrew Y. Ng, and Christopher D. Manning.
Semi-supervised recursive autoencoders for predicting sentiment distributions. In
EMNLP, 2011.
模型结构:
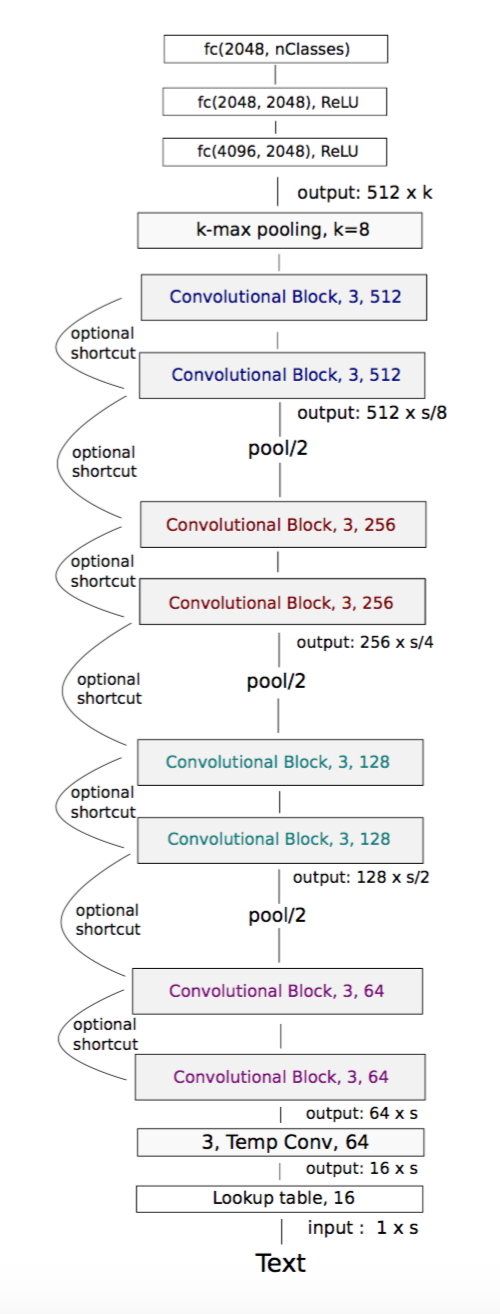
s 是时间窗长度,首先将字符embedding到16维的向量!
第一层64个特征,后续是ConvNet Block,采用下述策略(from VGG and ResNet):
- 如果时间分辨率不变,输入和输出特征维度相同
- 如果时间分辨率减半,输出特征维度加倍
更多的卷积层,意味着能够学习更长的依赖关系!并且,对所有的时间几乎是平等的!而不像RNN,LSTM那样!
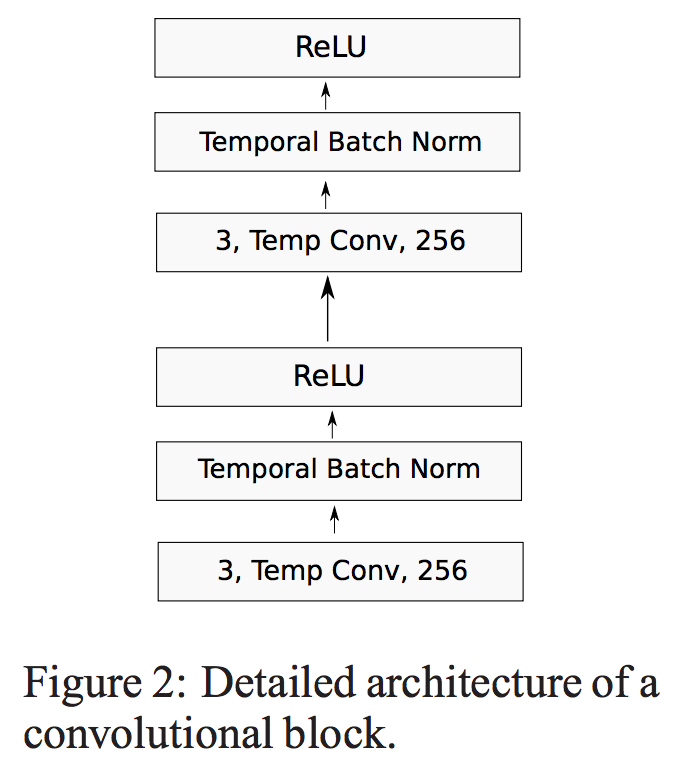
其中一个CNN Block 结构如图Fig.2。包含两个维度为3的核的卷积层,每个卷积层后跟一个BN层和一个非线性层!
多个小尺寸的卷积层可以用较少的参数实现一个大尺寸的卷积层相同的功能(视野和非线性度)!
输入字符增加了一个表示未知符号的特殊字符,一共72个token。输入文本padding到长度为1014!字符embedding到16维的向量。
其他参数:
- mini-batch of size 128
- initial learning rate of 0.01
- momentum of 0.9
- 每次验证集错误增加就将学习率减半
- 初始化采用 何凯明 的方案
- 采用 BN 而没有dropout
结论
- 在大数据集上有明显提升,即使深度较小
- 深度可以提升效果!
- Max-pooling 最优
- degradation:增加深度,性能下降,通过shortcut减少这种效果。
Exploring the impact of the depth of temporal
convolutional models on categorization tasks with hundreds or thousands of classes would be an
interesting challenge and is left for future research.
CNN 句子建模
A Convolutional Neural Network for Modelling Sentences,2014.
Dynamic Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN): 采用Dynamic k-Max Pooling,即pooling的时候,选取最大的k个值,而不是一个最大值。
采用多个滤波器,提取多个特征。
- Neural Bag-of-Words (NBoW) models:
- 投影层:将 word, sub-word, n-gram 映射到高维 embedding 向量。
- 组合:将这些向量组合(求和,均值,加权和等)
- 将组合后的向量作为句子的特征表达,传入全连接神经网络进行监督学习。
- Recursive Neural Network (RecNN):利用一个额外的 parse tree。
- 递归地组合叶子节点
- 将根节点的向量作为句子的特征表达,传入全连接神经网络进行监督学习。
- RNN:最为RecNN 的一个特例,即线性地组合相邻的向量,把最后节点对应的向量作为句子的特征向量。
- TDNN:Time delay,利用卷积。
一维卷积,即只对时间维度进行卷积。 TDNN对时间维度是卷积,对另一个维度(每个词都对应一个向量)则是全连接,并且采用窄版的卷积。
Max-TDNN解决可变长度问题:每一个滤波器,最终只得到一个特征,即对卷积后的序列只取一个最大值。最终有几个卷积核,特征的维度就是几。
最后得到的特征传入全连接神经网络进行监督学习。整个过程是联合优化的。
- 特点:对词序不敏感;不需要额外的语言特征(dependency tree,parse tree)。
- 缺点:首先于卷积的长度,相当于只考虑 m-gram 的词特征,长距离的词关联无法学到。一个 max-pooling 导致的问题:抹去了顺序的信息。
解决的办法:Dynamic k-max pooling
最后一层的k是固定的,保证最后一层的输出特征数目是定长的,但是中间的k是动态的。
$$
k_l = \max (k_{top}, \ceil{\frac{L - l}{L} s})
$$
L 是所有的卷积层数目,l是当前层的序号,s是句子长度,实际上是为了使得pooling是平滑的线性降低维度。
CNN句子分类
Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification,Kim 2014.
- 要点:
- 双通道,一个词向量通道可变,用于学习与目标有关的词向量(情感相关),另一个通道不可变,防止过拟合。
这个很关键,可以参看论文,解决 word2vec 反义词的问题。 - 时间卷积,在另一个维度求和
- max-over-time pooling
- dropout
- 双通道,一个词向量通道可变,用于学习与目标有关的词向量(情感相关),另一个通道不可变,防止过拟合。